What is the EGR system and which oil is suitable?
Posted by Hamid Shakouri on 3rd Sep 2024
To decrease the generation and emission of greenhouse gases especially NOX (Nitrogen Oxide Components) OEM company designed a new system called Exhaust Gas Recirculation or EGR.
In this system, a portion of exit gasses from the exhaust back into the engine cylinder to reduce the formation of NOx by lowering the combustion temperature.
This helps in decreasing overall greenhouse gas emissions from vehicles.
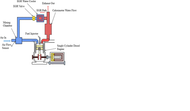
EGR diagram
EGR systems can increase the operating temperatures within the engine, including in the combustion chamber and exhaust system. These higher temperatures can accelerate the oxidation of the engine oil, leading to the formation of sludge, varnish, and other deposits. Additionally, the recirculation of exhaust gases can introduce contaminants into the engine oil, further stressing its stability.
On gasoline engines, the system also reduces fuel consumption when the engine is operated under partial load.
In the EGR diagram, a portion of exhaust gas will be cooled in the EGR water cooler by coolants. However, the warmer coolant cannot absorb a large part of the hot engine oil's temperature. Consequently, the temperature of the oil in the oil sump will rise by around 40°C compared to the same oil in a diesel engine without an EGR system. Therefore, engine oil must possess specific properties, including low soot, excellent oxidation, and thermal stability.
These properties are crucial for engine oils used in vehicles equipped with Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) systems. The increased temperature in the oil sump due to EGR operation can accelerate oil degradation, leading to issues such as increased viscosity, oxidation, and the formation of deposits.